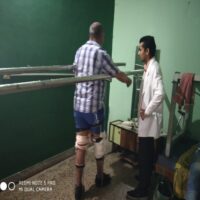
DDRC Started on 19/02/2013. We give service in Urban & Rural areas. This program is supported by Department for Empowerment of Differently Able and Senior Citizens, Government of Karnataka, Bangalore. To implement this program, District level monitoring team is functioning. The main activity of this committee is to cover local awareness camps, health check-up camps, and rehabilitation for the disabled, and this activity is exercised in all eight taluks of the Chickamagaluru District.
Professionals:
- Clinical Psychologist.
- Audiologist &Speech pathologist.
- Physiotherapist
- Social worker.
- Optometrist
Treatment & Services:
Occupational therapy & Physical therapy – services that relate to self-help skills, adaptive behavior and play, sensory, motor, and postural development i.e. services to
prevent or lessen movement’s difficulties and related functional problems. Sensory Integration, oro-motor and feeding difficulties. (Physiotherapist/Occupational therapist)
- Psychological services – administering and interpreting psychological tests and evaluation of a child’s behavior related to development, learning, and mental health as well as planning services including counseling, consultation, parent training, behavior modification, and knowledge of appropriate education programs. (Rehabilitation Psychologist/Clinical Psychologist).
- Cognition services – identifying cognitive delays and providing intervention to enhance cognitive development, adaptive and learning behaviors. (Clinical Psychologist and Early Interventionist)
- Audiological services – identifying and providing services for children with hearing loss among children from birth to 6 years for both congenital deafness and also acquired (Audiologist cum speech and language pathologist)
- Speech-language pathology – services for children with delay in communication skills or with motor skills such as weakness of muscles around the mouth or (Audiologist cum speech and language pathologist).
- Vision services – identification of children with visual disorders or delays and providing services and training to those children. (Optometrist). Retinopathy of Prematurity (RoP) – for premature or preterm children. (Optometrist and ophthalmologist)
- Health services – health-related services necessary to enable Patients to benefit from other (Doctor)Social support services – preparing an assessment of the social and emotional strengths and needs of a Patient and family, and providing individual or group services such as counseling. Socioeconomic evaluation of the family and linkages with the need-based social services. (Social Worker /Psychologist)
- Psycho-social services – include designing learning environments and activities that promote the child’s development, and providing families with information, skills, and support to enhance the child’s development. (Special Educator) Supplementary services.
- Assistive technology devices and services: equipment and services that are used to improve or maintain the abilities of a child to participate in such activities as Hearing, Seeing (Vision), Moving, Communication, and learning to compensate for a specific biological limitation.
- Special Education services: for School age groups from six to sixteen, Pre- Vocational training for ages 16-18 years, and Vocational training for the age of 18
- Aids and appliances: Assistance to Disabled Persons for Purchase / Fitting of Aids and Appliances under the “Assistance to Disabled Persons for Purchase/ Fitting of Aids/Appliances (ADIP)” Scheme, with the objective of assisting needy persons with disabilities in procuring durable, sophisticated and scientifically manufactured standard aids and appliances that can promote their physical, social and psychological rehabilitation.
- Rehabilitation of the differently abled: at the Rehabilitation centers in that state e.g. for the districts where they are functional or Composite Regional Centers (CRCs) or National Institutes/Regional Centers etc.
- Family support services: esp. for children having Autism, Cerebral palsy, Mental retardation, or multiple disabilities. These Services would be to support those children who would require long-term support and would focus on supporting the child in their natural environments and in their everyday experiences All services would be provided using a family-centered approach, recognizing the importance of working in partnership with the family.
- Health Awareness: Health Awareness Camps amounting to 050 Camps in which 1010 beneficiaries Nodal Officer, DDRC, Chickamagalur & Medical Officers and paramedical staff of the respective PHC Hospitals were taken participated as Service providers. In these camps, Disabled persons have been identified for free supply of aids and appliances. These awareness camps are being conducted every Tuesday and the first and second week Fridays of every month. In the camps, medical experts like psychiatrists, audiologists, SLP, ENT specialists, Orthopedics, and Opthalmist including Clinical psychologists are taking participate and identifying the patient’s problems, and referring the case to the concerned Medical Institutions.
- Health Check-up: Health Check-up camps amounting to 56 Camps with which 1393 beneficiaries Out of which 140 were identified for treatment of which 123 persons were referred. The Resource Persons are Nodal Officers, DDRC, Medical Officers & Paramedical staff of Taluk Hospitals. In these Health Check-up camps the Medical Specialists from the Taluk hospital together with their paramedical staff are taking participate to screen asses diagnoses and at-site treatment is given. Referral cases are also exercised. To Provide UDID CARD 793 Members.
- Education Scholarship: 023 persons were identified out of which 023 persons were granted.
- The Disabled identification certificates: with other members of the disability board 077 identified: 069 identification Cards issued.
- Niramaya Health Scheme: 087 persons identified: 032 persons issued with the cards. were identified for which beneficiaries have been issued the cards. The Niramaya Scheme covers the patients (Disabled Persons) Mentally Retarded, Multiple Disability, and Cerebral Palsy & Autism.
21 Characteristics Disabilities:
- Blindness: Blindness is defined as the state of being sightless. A blind individual is unable to see. In a strict sense, the word blindness denotes the condition of total blackness of vision with the inability of a person to distinguish darkness from bright light in either eye.
- Low-vision: Low-vision means a condition where a person has any of the following conditions, namely:
- visual acuity not exceeding 6/18 or less than 20/60 upto 3/60 or up to 10/200 (Snellen) in the better eye with best possible corrections; or
- limitation of the field of vision subtending an angle of less than 40 degrees up to 10 degrees.
- Leprosy Cured Persons: Leprosy, also known as Hansen’s disease (HD), is a chronic infectious disease caused by a bacteria called Mycobacterium leprae. The disease mainly affects the skin, the peripheral nerves, mucosal surfaces of the upper respiratory tract and the eyes. Leprosy is known to occur at all ages ranging from early infancy to very old age. About 95% of people who contact M. Lepreado does not develop the disease.
- Hearing Impairment: Hearing impairment is a partial or total inability to hear. It is a disability that is sub-divided into two categories deaf and hard of hearing.
- “Deaf” means persons having 70 dB hearing loss in speech frequencies in both ears.
- “Hard of hearing” means person having 60 dB to 70 dB hearing loss in speech frequencies in both ears.
- Locomotor Disability: Strictly speaking Locomotor Disability means problem in moving from one place to another — i.e. disability in legs. But, in general, it is taken as a disability related with bones, joints and muscles. It causes problems in person’s movements (like walking, picking or holding things in hand etc.)
- Dwarfism: Dwarfism is a growth disorder characterized by shorter than average body height.
- Intellectual Disability: Intellectual disability, also known as general learning disability and mental retardation (MR), is a condition characterized by significant limitation both in intellectual functioning (reasoning, learning, problem solving) and in adaptive behavior which covers a range of every day, social and practical skills.
- Mental Illness: Mental illness or mental disorder refers to a substantial disorder of thinking, mood, perception, orientation or memory that grossly impairs judgment, behavior, capacity to recognize reality or ability to meet the ordinary demands of life. But it does not includeretardation which is a condition of arrested or incomplete development of mind of a person, specially characterized by sub-normality of intelligence.
- Autism Spectrum Disorder: Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurological and developmental disorder which affects communication and behavior. Autism can be diagnosed at any age. But still it is called a “developmental disorder” because symptoms generally appear in the first two years of life. Autism affects affects the overall cognitive, emotional, social and physical health of the affected individual.
- Cerebral Palsy: Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a disabling physical condition in which muscle coordination is impaired due to damage to the brain. It occurs at or before child birth. Cerebral Palsy is not a progressive condition; meaning it does not get worse with time. However, muscle disuse could increase the extent of disability over the period of time. At present there is no cure available for this condition. Thus, Cerebral Palsy is incurable and life-long condition, at present.
- Muscular Dystrophy: Muscular Dystrophy (MD) is a group of neuromuscular genetic disorders that cause muscle weakness and overall loss of muscle mass. MD is a progressive condition; meaning that it gets worse with the passage of time.
- Chronic Neurological Conditions
Examples of Chronic Neurological Conditions:
- Alzheimer’s disease and Dementia
- Parkinson’s disease
- Dystonia
- ALS (Lou Gehrig’s disease)
- Huntington’s disease
- Neuromuscular disease
- Multiple sclerosis
- Epilepsy
- Stroke
- Specific Learning Disabilities: Specific Learning Disabilities is a group of disabling conditions that hampers a person’s ability to listen, think, speak, write, spell, or do mathematical calculations. One or more of these abilities may be hampered.
- Multiple Sclerosis: In Multiple Sclerosis (MS), the immune system of body attacks the Central Nervous System, which includes brain and spinal cord. As a result of MS, the myelin sheathcovering on neurons gets damaged. This exposes the nerve fiber and causes problems in the information flow through nerves. With time, MS can lead to the permanent damage to nerves.
- Speech and Language Disability: A permanent disability arising out of conditions such as laryngectomy or aphasia affecting one or more components of speech and language due to organic or neurological causes.
- Thalassemia: Thalassemia is a genetically inherited blood disorder which is characterized by the production of less or abnormal hemoglobin. As we know, hemoglobin is a protein found in Red Blood Cells. Hemoglobin is responsible for carrying oxygen around in the body. Thalassemia results in large numbers of red blood cells being destroyed, which leads to anemia. As a result of anemia, person affected with Thalassemia will have pale skin, fatigue and dark coloration of urine.
- Hemophilia : Hemophilia is a blood disorder characterized by the lack of blood clotting proteins. In the absence of these proteins, bleeding goes on for a longer time than normal. Hemophilia almost always occurs in males and they get it from their mothers. Females are rarely affected with hemophilia.
- Sickle Cell Disease: Sickle Cell Disease is a group of blood disorders that causes red blood cells (RBCs) to become sickle-shaped, misshapen and break down. The oxygen-carrying capacity of such misshapen RBCs reduce significantly. It is a genetically transferred disease. Red Blood Cells contain a protein called hemoglobin. This is the protein that binds oxygen and carry it to all the parts of the body.
- Multiple Disabilities including Deaf-blindness: Multiple Disabilities is the simultaneous occurrence of two or more disabling conditionsthat affect learning or other important life functions. These disabilities could be a combination of both motor and sensory nature.
- Acid Attack Victims: An acid attack victim means a person disfigured due to violent assaults by throwing of acid or similar corrosive substance.
- Parkinson’s disease: Parkinson’s disease (PD) is Central Nervous System disorder which affects movement. Parkinson’s disease is characterized by tremors and stiffness. It is a progressive disease, which means that it worsens with time. There is no cure available at present.
Services Provided in:
- Schools
- Special School.
- Primary Health Care Centers.
- Anganavadis
- Government Hospitals.
- Grama Panchayaths.
- Nagarasabhe Patana Panchayath.